Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is IO-Link?
In this article, we are going to learn about IO-Link.
IO-Link is a communications protocol that works point-to-point.
A point-to-point communication connection is a communications connection between two separate endpoints or nodes.
IO-Link is bi-directional which means it works two ways and works over a short distance. It is primarily used to communicate with sensors and actuators in plant or factory automation processes.

Sensors and actuators are usually connected via field bus connections, allowing them to be in remote locations. With IO-Link, the field devices, such as actuators or sensors, connect to a master device, which communicates to a controller, usually a PLC or Programmable Logic Controller.
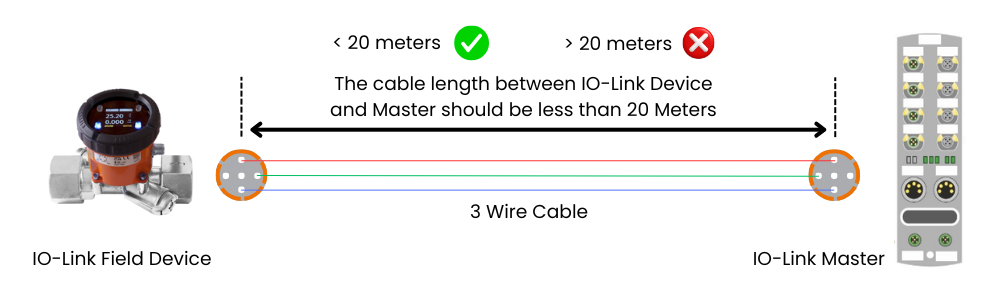
The connection between the IO Link Master and the field device is done via a 3-wire cable. The cable should not be more than 20 meters long.
The IO Link Master is capable of processing digital signals and analog values.
It can integrate into existing systems and can communicate using the industry recognized PROFINET, PROFIBUS, or MODBUS to name a few. The IO Link Master establishes the connection between the IO-Link devices and the automation system.
As a component of an IO system, the IO Link Master is installed either in the control cabinet or as remote IO, directly in the field.
An IO Link Master can have several IO Link ports or channels.
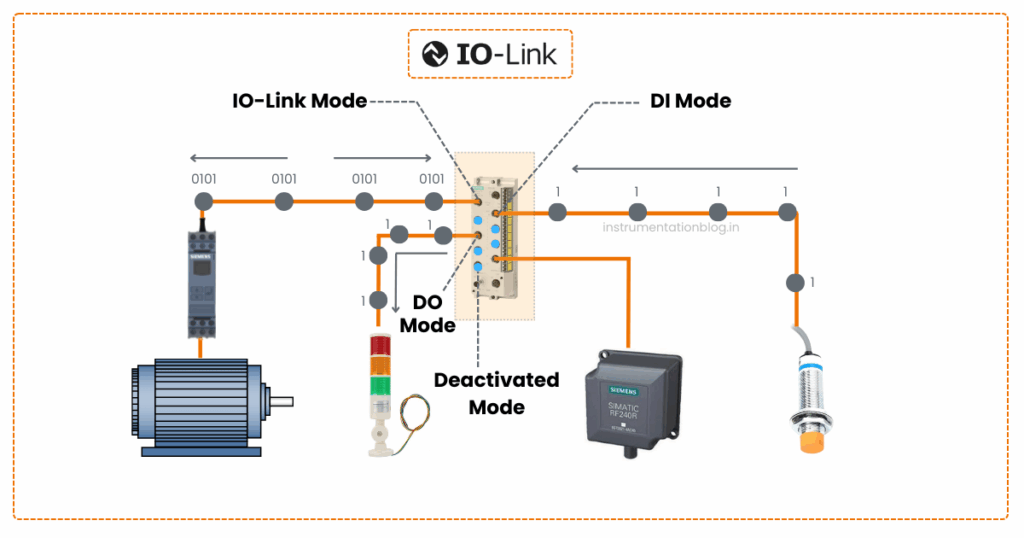
Four different operating modes
1) The first mode is the IO-Link mode. This means that the port is used for IO-Link communication.
2) The second mode is the DI mode. This means that the port acts in the same way as a digital input device.
3) The third mode is the DO mode. This means that the port acts in the same way as a digital output device.
4) The fourth mode is deactivated. This means that the port is not assigned to any other modes and is reserved for when the port is unused.
Please see below schematic with different operating modes.
IO-Link is a very robust communication system that operates using 24 volts.
The transmission errors can occur for so many reasons. In general, a cable fault or a power surge can temporarily interfere with transmissions. If an error is detected, the message attempts transmission up to an additional two times. Only after the transmission has failed for a third time does the IO-Link Master recognize a communication failure. Upon recognizing this, the IO-Link Master will signal the communications failure to the higher-level controller. This can then alert operators or maintenance staff of the issue so they can physically attend to and rectify the problem.

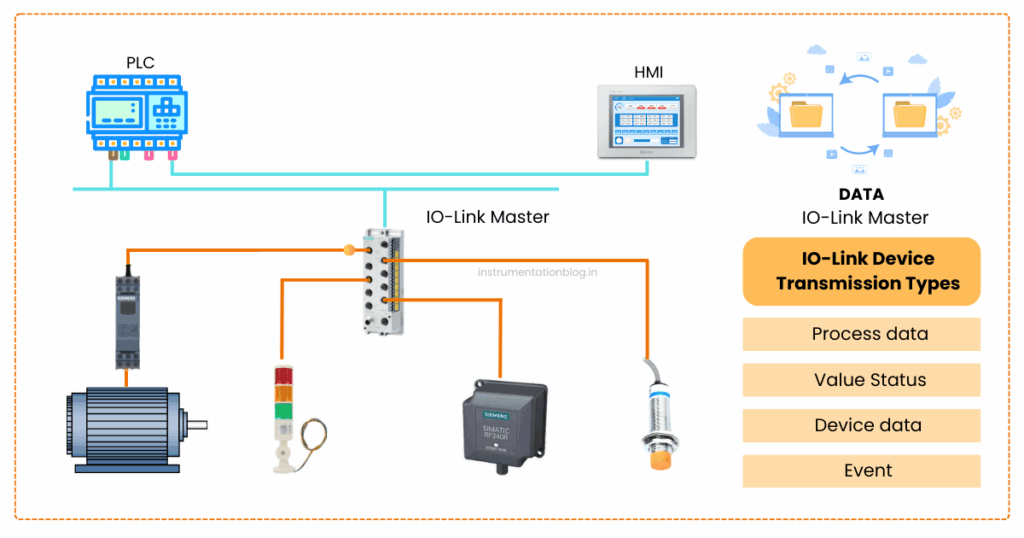
Four types of IO-Link device transmissions
An IO-linked device has four types of transmission.
1) Process data
2) Value status
3) Device data
4) Events.
The process data is considered as the latest state of the sensor or actuator, such as speed. Process data is transmitted cyclically, which means automatically, at regular defined intervals. Up to 32 bytes of process data can be processed.
and it’s defined by the high-level controller. The value status indicates whether the processed data is valid or invalid and is transmitted along with the processed data cyclically. The device data holds detailed information about a device.
Basic information such as the serial number or version number and more advanced information such as parameters or diagnostic information can be retrieved from each IO-Link device.
Device data is transmitted at the request of the IO-Link master. This means that it is not automatically transmitted but will be transmitted after a request from the IO-Link master. Device data can be read from the device but also written to.
A device can trigger an event, which in turn signals the presence of an event to the IO-Link master.
An example of an event is an error or warning message,
As an example consider a short circuit or device that is overheating. This information can be used to display indicators or messages on HMI devices, such as error messages signaling a wire break or a communication failure, once the IO-Link master has processed the message to the high-level controller.
The transmission of device parameters and events occurs independently from the cyclic transmission of process data. This means that they do not impact each other, so critical messages do not have to queue until already buffered messages are sent.
Checking the field device’s instructions is a necessity to be able to communicate correctly. Don’t worry though, once it’s set up, they are very easy to maintain and often work seamlessly with no additional work required. Want to learn PLC programming in an easy-to-understand format and take your career to the next level
I love helping you learn. So, if you enjoy this article as much as I enjoyed making it, please share the article in your network.
Understanding the IO-Link Standard
IO Link follows the IEC 61131-9 standard, which is also used worldwide for programming PLCs. An IO-Link Consortium supports and promotes this standard, making it easier for different companies to create sensors and actuators that can work together in smart factory systems and IoT platforms.
Benifits of IO-Link
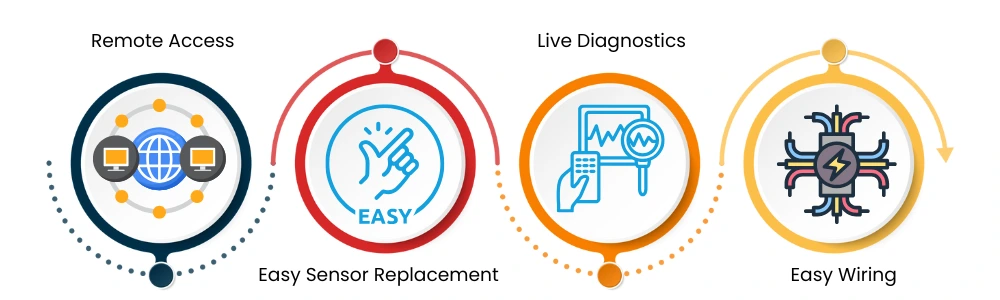
IO Link have different advantages as below:
Remote Access: IO Link allows settings and configurations to be adjusted from anywhere, just like other elements in a connected machine platform. This makes maintenance and changes much easier.
Easy Sensor Replacement: IO Link automatically transfers the settings from a failed sensor to a new one. This makes replacements quick and hassle-free.
Live Diagnostics: IO Link provides real-time diagnostic data without needing to stop the machine. This helps detect and fix problems faster, minimizing downtime.
Easy Wiring: IO Link devices use standard unshielded 3-wire cables, similar to regular I/O wiring. This makes installation process very easy and also reduces the cost.
So these are some basic concepts about IO-Link. If you like this article please feel free to share in your network.
I hope you like above blog. There is no cost associated in sharing the article in your social media. Thanks for reading!! Happy Learning!!


