Table of Contents
ToggleIf you have ever connected a PLC to a VFD, an energy meter, a temperature controller, or even a simple weighing indicator, you must have seen two common communication options: RS232 and RS485.
Both are called serial communication, but in real plant conditions they behave very differently. Choosing the wrong one can lead to unstable data, random communication faults, and lots of troubleshooting time.
RS232 is mainly for short and direct connections, while RS485 is made for long-distance and multi-device industrial networks.
That is the basic idea behind RS232 vs RS485. Now let us understand why this difference exists.

What RS232 and RS485 actually mean?
RS232 and RS485 are electrical interface standards. They define how electrical signals are sent on wires, not how the data itself is structured.
They mainly define:
Voltage levels used for communication
How signals are referenced to ground
How many devices can connect on the same line
How far the signal can travel reliably
Protocols like Modbus RTU, ASCII, or proprietary PLC protocols run on top of RS232 or RS485.
So when we talk about RS232 vs RS485, we are talking about the physical layer, not the software protocol.
Communication structure and number of devices
One of the biggest differences between RS232 vs RS485 is how many devices can talk on the same cable.
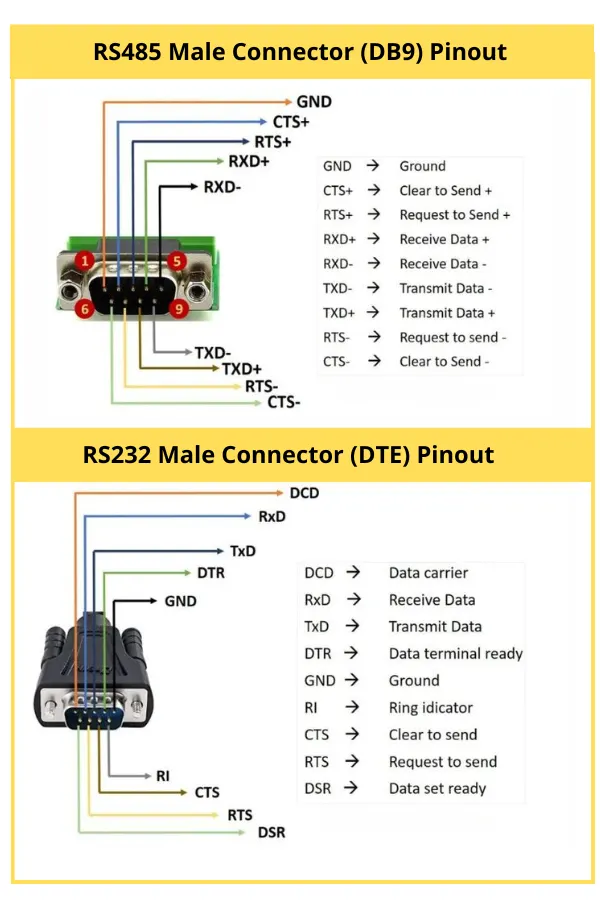
RS232 communication structure
Point-to-point only – one transmitter and one receiver
Only two devices can communicate directly
Not suitable for networking multiple field devices
This is why RS232 is mostly used between a PC and one instrument, or between two devices located very close to each other.
RS485 communication structure
Multi-drop network – one master can communicate with many slaves
Several devices can share the same communication line
Ideal for field-level networks such as Modbus RTU
This makes RS485 perfect for connecting multiple meters, drives, and controllers on a single cable in industrial automation.
Signal type and noise immunity
Industrial plants are full of electrical noise from motors, contactors, and variable frequency drives. This is where RS232 vs RS485 becomes very important.
RS232 signal behavior
Uses single-ended signaling
Signal is measured with respect to ground
Any ground noise or voltage shift can disturb the signal
Because of this, RS232 works well only in clean electrical environments and short distances.
RS485 signal behavior
Uses differential signaling with two opposite polarity wires
Receiver reads the voltage difference between the two wires
Noise affecting both wires gets cancelled out
This is why RS485 is much more resistant to EMI and is preferred in harsh industrial environments.
Communication distance capability
Distance is another practical factor when comparing RS232 vs RS485.
RS232 distance limitations
Designed for short cable runs
Typically reliable up to around 10 to 15 meters
Longer distances increase error probability
RS485 distance capability
Designed for long cable runs
Can reach several hundred meters and even more with proper wiring
Works well in large plants and outdoor installations
So if your instrument is installed far from the control panel, RS485 is almost always the better choice.
Wiring complexity and cable requirement
Wiring may look simple, but it plays a huge role in communication stability.
RS232 wiring characteristics
Requires separate transmit and receive lines
Needs common ground reference
Often uses DB9 connectors or multi-core cables
RS485 wiring characteristics
Usually uses only one twisted pair for data
Supports daisy-chain wiring between devices
Screw terminals are common in industrial instruments
This is why RS485 networks are easier to expand and maintain in field installations.
Duplex communication behavior
Another technical but important difference in RS232 vs RS485 is how data flows.
RS232 communication mode
Full duplex by default
Sending and receiving can happen at the same time
Separate wires for transmit and receive
RS485 communication mode
Can be full duplex or half duplex
Most industrial networks use half duplex
Only one device transmits at a time
This is why proper protocol timing is important in RS485 networks to avoid data collisions.
Termination and network stability
This is one area where many field engineers face trouble with RS485.
RS232 termination behavior
No termination resistors required
Simple point-to-point wiring
RS485 termination requirement
Termination resistors are needed at both ends of the cable
Prevents signal reflection on long cables
Bias resistors may be needed to avoid floating lines
In RS232 vs RS485, RS485 gives better performance but needs more care in wiring practices.
Typical industrial applications
Understanding where each standard is used makes the RS232 vs RS485 difference very clear.
Where RS232 is commonly used
Laptop to PLC or instrument for configuration
Printer or display connected to one controller
Short internal panel connections
Where RS485 is commonly used
Modbus RTU networks in plants
Multiple energy meters connected to SCADA
VFD and temperature controller networks
Remote field devices over long cable distances
That is why most industrial communication networks prefer RS485.
Selection guide for engineers and technicians
If you are selecting communication for a new project, keep this simple logic in mind.
If there is only one device and the cable is short, RS232 is sufficient.
If there are many devices on one line, RS485 is required.
If the environment has electrical noise, RS485 is safer.
If the distance is more than a few meters, RS485 is the better choice.
In industrial automation, this rule solves most RS232 vs RS485 selection problems.
Common mistakes seen in RS485 installations
Even though RS485 is strong, wrong installation can create problems.
Star topology instead of proper daisy-chain wiring
Missing termination resistors at cable ends
Wrong A and B line polarity connections
Running communication cable together with power cables
No proper grounding reference in long networks
Most communication failures blamed on devices are actually wiring issues.
What we learn today?
Both RS232 and RS485 are useful, but they are designed for different purposes. RS232 is simple, direct, and suitable for short links. RS485 is designed for industrial networking, long distances, and noisy environments.
So when choosing between RS232 vs RS485, think about distance, number of devices, and plant conditions. In most industrial automation systems, RS485 becomes the natural and safer choice for stable communication.
I hope you like above blog. There is no cost associated in sharing the article in your social media. Thanks for Reading !! Happy Learning