Table of Contents
ToggleCommon Types of Thermocouples: Introduction
Temperature measurement is one of the most important parameters in the instrumentation world. From boilers and furnaces to food processing plants and cryogenic tanks, accurate temperature monitoring keeps processes safe, efficient, and reliable.
Among all temperature sensors, thermocouples are one of the most widely used devices in industry.
In this article, we will clearly explain the common types of thermocouples and their ranges, how they work, where they are used, and how to choose the right one for your application.
Let’s start with the basics.
What Are Thermocouples?
A thermocouple is a temperature sensor made of two dissimilar metal wires joined at one end. When this junction experiences a temperature difference compared to the other end, it generates a small voltage. This phenomenon is called the Seebeck Effect.
This voltage is proportional to temperature, and a temperature measuring instrument converts it into a readable value.
Key Features of Thermocouples
Wide Temperature Range
Thermocouples can measure extremely low and extremely high temperatures. This is one reason they are preferred over RTDs in high-temperature applications.Fast Response Time
Because of their small mass and simple construction, thermocouples respond quickly to temperature changes.Durability and Ruggedness
Thermocouples are robust and can withstand vibration, pressure, and harsh industrial environments.
Now let us explore the common types of thermocouples and their ranges in detail.
Common Types of Thermocouples and Their Ranges
Different thermocouple types are identified by letters such as K, J, T, E, N, S, R, and B. Each type has a specific metal combination and temperature range.
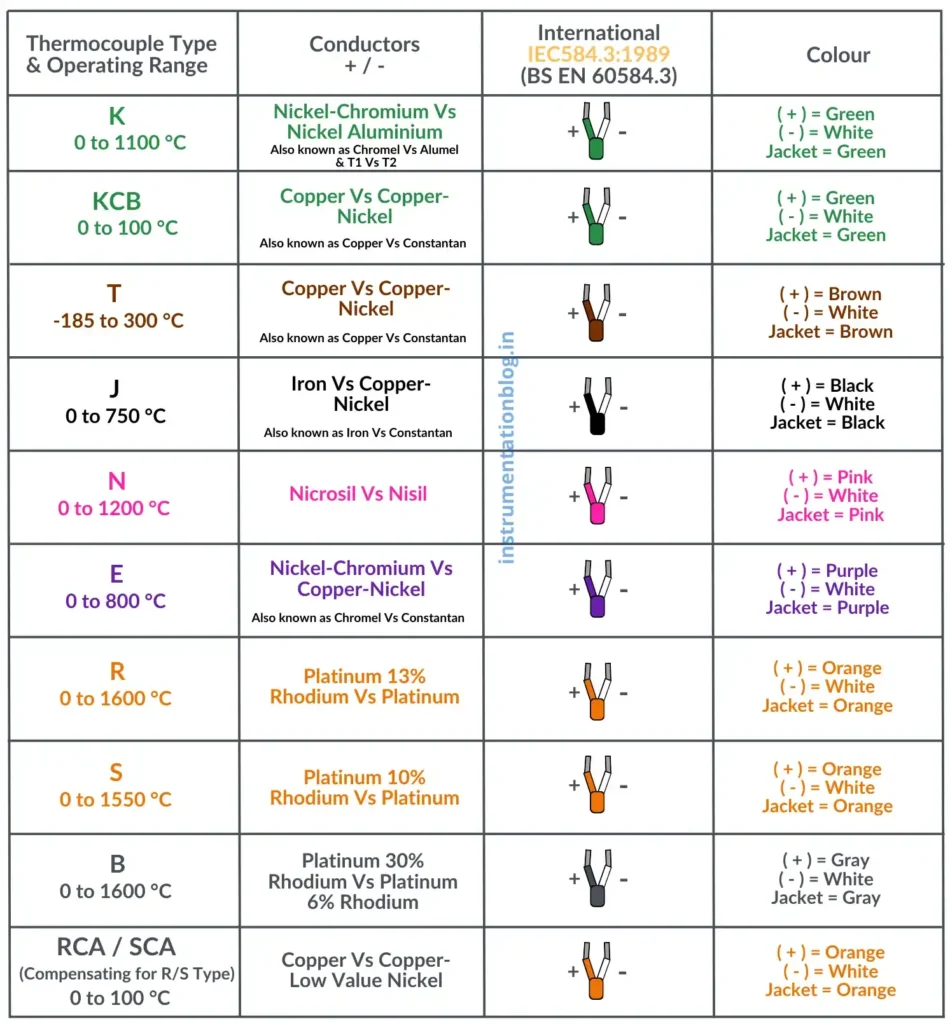
K-Type Thermocouple
Temperature Range: –200 °C to 1260 °C
Type K is the most commonly used thermocouple in industry.
Why is Type K Popular?
Wide Temperature Range
It covers both low and high temperatures.Good Accuracy and Stability
Suitable for general-purpose industrial applications.Oxidation Resistant
Performs well in oxidizing atmospheres.
Typical Applications
Furnaces
Boilers
Gas turbines
Heat treatment plants
If someone asks about the most versatile option among the common types of thermocouples and their ranges, Type K is usually the first answer.
J Type Thermocouple (Iron–Constantan)
Temperature Range: –40 °C to 750 °C
Type J thermocouples are commonly used in moderate temperature environments.
Important Characteristics
Lower Cost
Iron-based construction makes it economical.Good Sensitivity
Suitable for many industrial processes.Oxidation Limitation
Iron oxidizes at higher temperatures, limiting its use in high-temperature environments.
Applications
Vacuum furnaces
Plastic molding
Heat treatment (low to medium temperature)
T Type Thermocouple (Copper–Constantan)
Temperature Range: –200 °C to 350 °C
Type T is excellent for low-temperature measurement.
Key Advantages
Excellent Low-Temperature Accuracy
Ideal for cryogenic applications.Stable and Reliable
Good performance in moist environments.Tight Accuracy Limits
±1°C or ±0.75% (whichever is greater), as per ANSI/ASTM E230.
Applications
Cryogenic storage
Food processing
Laboratory freezers
Among the common types of thermocouples and their ranges, Type T is the best choice for sub-zero measurements.
E Type Thermocouple (Chromel–Constantan)
Temperature Range: –200 °C to 900 °C
Type E thermocouples generate the highest EMF (output voltage) among base metal thermocouples.
Key Benefits
High Output Voltage
Better signal strength.Good Accuracy
±1.7°C or 0.5%.Suitable for Cryogenic Use
Applications
Low-temperature systems
Chemical processing
Industrial ovens
N Type Thermocouple (Nicrosil–Nisil)
Temperature Range: –200 °C to 1300 °C
Type N is considered an improved alternative to Type K.
Why Choose Type N?
Better Stability at High Temperature
Improved Resistance to Drift
Longer Life in Industrial Applications
Applications
High-temperature furnaces
Petrochemical plants
Industrial reactors
When comparing common types of thermocouples and their ranges, Type N is often selected where long-term stability is important.
S Type Thermocouple (Platinum–Rhodium)
Temperature Range: 0 °C to 1480 °C
Type S belongs to the noble metal thermocouple family.
Characteristics
High Accuracy
Excellent Stability
Expensive Material
Applications
Laboratories
High-quality manufacturing
Glass and ceramics industry
R Type Thermocouple (Platinum–Rhodium)
Temperature Range: 0 °C to 1600 °C
Type R is similar to Type S but with a higher temperature capability.
Applications
Steel manufacturing
High-temperature furnaces
Critical industrial processes
B Type Thermocouple (Platinum–Rhodium)
Temperature Range: 0 °C to 1700 °C
Type B is designed for extremely high temperatures.
Key Benefits
Very High Temperature Capability
Excellent Stability
Used in Extreme Industrial Environments
Applications
Industrial kilns
High-temperature research
Metal processing plants
Among the common types of thermocouples and their ranges, Type B handles the highest temperature.
How to Choose Between Different Types?
Selecting from the common types of thermocouples and their ranges is not just about temperature. You must consider several factors.
Temperature Range
Always match the thermocouple type to your operating temperature.
For example:
Type T: Maximum around 370°C (depending on wire size)
Type K: Up to 1260°C
Type B: Up to 1700°C
Conductor Size
Wire diameter affects temperature rating and durability.
Example:
#14 AWG Type T → Rated up to 370°C
#30 AWG Type T → Limited to around 150°C
Thinner wires respond faster but cannot handle high temperatures for long durations.
Accuracy
Accuracy varies by type:
Type T → ±1°C or ±0.75%
Type E → ±1.7°C or 0.5%
Types J, K, N → ±2.2°C or 0.75%
For precision measurement, noble metal types (S, R, B) are preferred.
Environment and Materials
Also consider:
Sheath material (SS, Inconel, ceramic)
Insulation type
Probe design
Corrosive or oxidizing atmosphere
Thermocouple Selection Based on Process Application
Selecting a thermocouple based only on temperature range is one of the most common mistakes in industry.
In real applications, the process environment is also very important. A thermocouple that works perfectly in one plant may fail quickly in another, even at the same temperature.
To select the right thermocouple based on process application, consider the following practical factors:
1. Process Atmosphere
The surrounding atmosphere directly affects thermocouple life.
In oxidizing environments such as boilers and general furnaces, Type K and Type N are commonly used because they perform well in oxygen-rich conditions.
In reducing or vacuum atmospheres, material compatibility becomes critical. Some thermocouple types may deteriorate quickly if the environment attacks the alloy.
For corrosive environments, sheath material selection (Inconel, stainless steel, ceramic) becomes equally important.
2. Continuous vs. Intermittent Operation
Is the process running 24/7 or only occasionally?
For continuous high-temperature processes such as petrochemical heaters or reformers, stability and resistance to drift are very important. Type N is often preferred over Type K in long-duration high-temperature applications.
For intermittent heating cycles, a standard Type K may be sufficient.
3. Low-Temperature and Cryogenic Applications
In food processing, pharmaceutical storage, or cryogenic tanks, accuracy and stability at low temperatures are critical.
Type T thermocouples are commonly selected for these applications because they offer excellent performance in sub-zero conditions.
4. High-Temperature Precision Applications
In glass plants, steel manufacturing, and laboratory furnaces, temperature can exceed 1400°C.
In such processes, noble metal thermocouples such as Type S, Type R, or Type B are selected. These provide better stability and accuracy at extreme temperatures, although at a higher cost.
5. Mechanical Conditions
Is there vibration? High pressure? Flow turbulence?
In applications such as engines, turbines, or rotating equipment, mechanical strength matters. Probe diameter, sheath thickness, and mounting design must be considered to prevent mechanical failure.
Thinner probes give faster response but are less durable.
6. Required Accuracy
If the process demands tight temperature control (for example, heat treatment or specialty manufacturing), thermocouple tolerance class becomes important.
For general monitoring, standard limits of error may be acceptable.
For critical processes, higher-grade or noble metal thermocouples may be required.
7. Maintenance and Replacement Cost
In some plants, thermocouples are easy to replace. In others, replacement requires shutdown and production loss.
In difficult-to-access installations, selecting a more stable and longer-lasting thermocouple type reduces long-term maintenance cost.
What we learn today?
Understanding the common types of thermocouples and their ranges is essential for selecting the right temperature sensor.
Each type has its own advantages:
Type K → General-purpose
Type J → Economical medium range
Type T → Low temperature
Type E → High output
Type N → Better stability
Type S, R, B → High-temperature precision
By matching temperature range, accuracy, environment, and mechanical design, you can select the right thermocouple for reliable and long-lasting performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the most common types of thermocouples used in industry?
The most common types of thermocouples and their ranges used in industry are Type K, Type J, Type T, Type E, and Type N.
For high-temperature precision applications, Type S, Type R, and Type B are also widely used.
Type K is the most popular because of its wide temperature range and good durability.
2. What is the temperature range of a Type K thermocouple?
Type K thermocouples operate from –200°C to 1260°C.
They are suitable for general industrial applications such as furnaces, boilers, and heat treatment processes.
3. Which thermocouple is best for cryogenic applications?
Type T thermocouples are best for cryogenic applications.
They work from –200°C to 350°C and provide excellent stability and accuracy at low temperatures.
4. Which thermocouple can measure the highest temperature?
Among the common types of thermocouples and their ranges, Type B can measure the highest temperature — up to 1700°C.
It is commonly used in industrial kilns, glass production, and metal processing.
5. What is the difference between base metal and noble metal thermocouples?
Base metal thermocouples include Type K, J, T, E, and N.
They are affordable and suitable for general industrial use.
Noble metal thermocouples include Type S, R, and B.
They use platinum-based materials, provide higher accuracy, and are used for extreme high-temperature applications.
6. How accurate are thermocouples?
Accuracy depends on the type:
Type T → ±1°C or ±0.75%
Type E → ±1.7°C or 0.5%
Types J, K, N → ±2.2°C or ±0.75%
For very high accuracy, noble metal thermocouples (S, R, B) are preferred.
I hope you like above blog. There is no cost associated in sharing the article in your social media. Thanks for Reading !! Happy Learning



