Today we are going to discuss about PLC Block Diagram. By the end, you will easily understand how a PLC works just by looking at its block diagram.
PLC stands for Programmable Logic Controller. It is one of the most widely used technologies in industries for automation.
Before PLCs were introduced, industries used analog control systems (which were harder to change and maintain). PLCs replaced them with a digital control system that is faster, more reliable, and easier to handle.
In simple words, a PLC is like a special computer designed for factories and manufacturing plants. Its main job is to control machines and processes automatically. The best part is that a PLC is very flexible, you can reprogram it anytime if the process or machine requirements change.
So, you can think of a PLC as the brain of industrial automation, making everything run smoothly and efficiently.
Table of Contents
TogglePLC Block Diagram
Please see below PLC Block Diagram. By looking at this diagram, you can easily understand the overall concept and the working process of a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC).
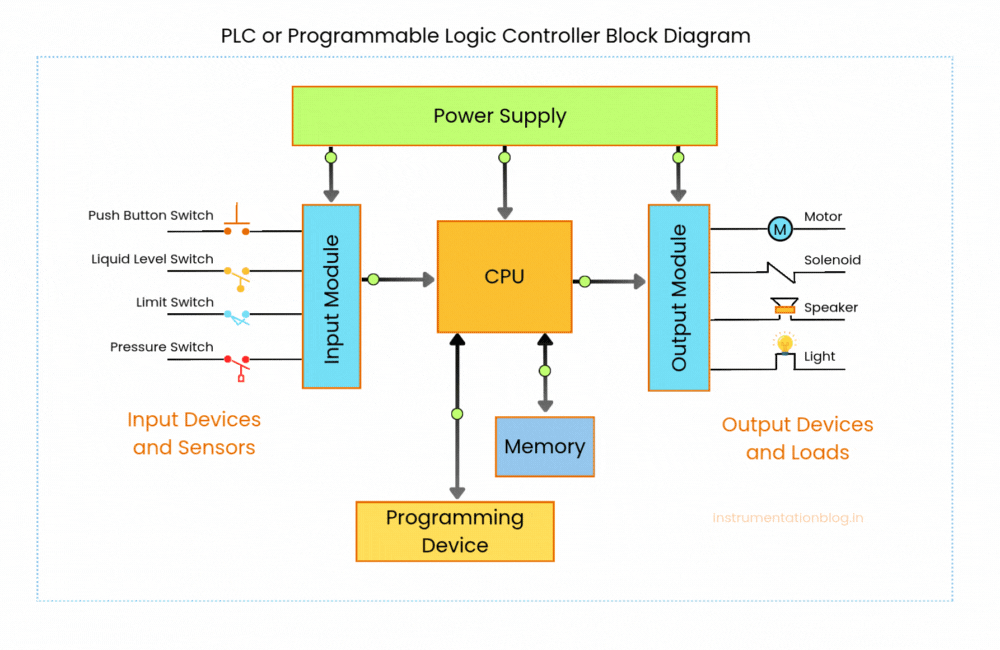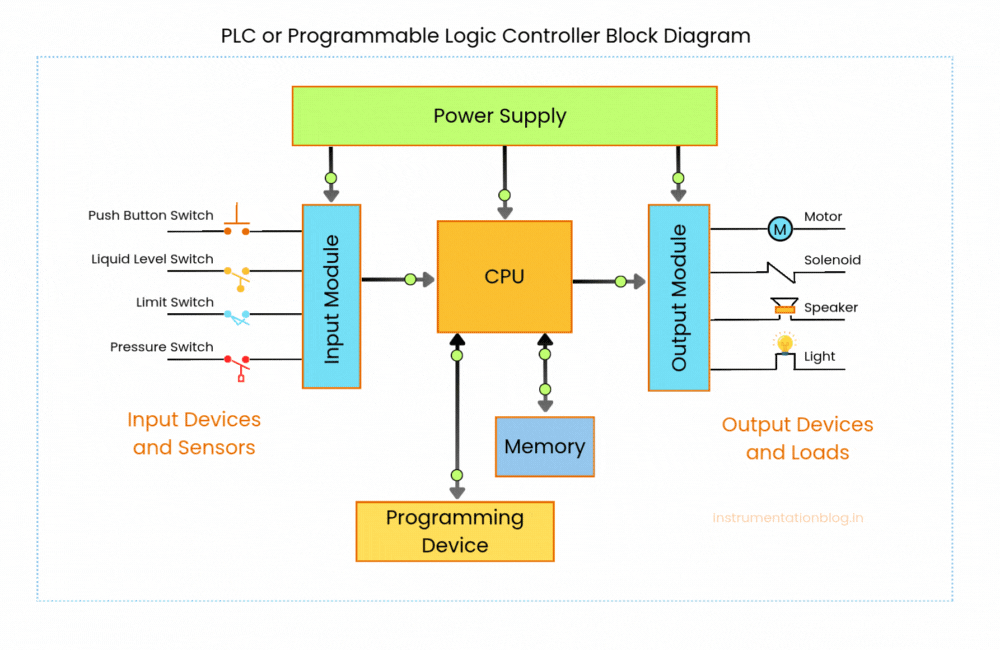
Above PLC block diagram shows how the input modules are connected to input devices like sensors, switches, and buttons, and how the output modules are connected to output devices like motors, lamps, and actuators. This makes it clear how a PLC communicates with the outside world.
The PLC Block diagram also highlights the CPU (Central Processing Unit) of the PLC. The CPU is like the brain of the system. It receives signals from the input devices, processes them according to the program (the logic written inside the PLC), and then sends the proper signals to the output devices through the output module.
In short, the PLC Block diagram explains the main job of a PLC: to take inputs, make decisions, and control outputs automatically.
Important Parts of a PLC System
As you can see in the block diagram, a PLC is mainly made up of the following important parts:
- Input Module
- Output Module
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Memory
- Power Supply Module
The CPU is the brain of the PLC. It is usually built using a microprocessor or microcontroller. The CPU does not work on its own it needs a program. This program is written on an external computer and then loaded into the PLC.
Once the program is installed, the PLC follows it step by step to perform its tasks and control the machines or processes automatically.
Working Principle of PLC
Now, let us go through each block of the PLC one by one. This will help you clearly understand the working principle of a Programmable Logic Controller.
CPU : Central Processing Unit
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the main part of the PLC. You can think of it as the brain of the system.
First, the program or instructions are stored in the memory. During operation, the CPU reads the signals from the input module, processes them according to the stored program, and then sends the result to the output module to control devices like motors, lamps, or valves.
The CPU performs many important jobs in a PLC, such as:
- Running the program step by step
- Processing data from inputs
- Communicating with other devices
- Managing memory and stored instructions
- Checking for errors and handling faults
- Controlling processes in real time
- Providing timing and synchronization
- Ensuring security and access control
In short, the CPU makes all the decisions inside a PLC.
Memory
The memory in a PLC is like its storage space. It keeps all the programs, data, and instructions that the PLC needs to work.
There are different types of memory inside a PLC:
- Program Memory – stores the PLC’s operating system, firmware, and the user’s program (the logic you create).
- Data Memory – stores values such as variables, counters, timers, and other data needed while the program runs.
- I/O Memory – stores the information exchanged between the PLC and the connected input/output modules.
Some PLCs also allow extra memory to be added using memory cards or external memory modules. This gives the PLC more space to handle bigger and more complex tasks.
Programming Device
The programming device is the tool used to write and store the program (instructions) into the PLC’s memory. This device is usually a computer or laptop.
PLC programs are created using special software provided by the PLC manufacturer. This software runs on a normal computer operating system (like Windows) and gives you an easy interface to:
- Create and edit the PLC program
- Organize the program into steps
- Configure input and output modules
- Set communication settings
- Test and troubleshoot the program
Once your program is ready, you can transfer it from the computer to the PLC hardware, where it will run and control the process.
Input and Output Module
The CPU or microprocessor inside the PLC works with a small voltage, usually 5V DC, and it can only handle a very small current. But in the real world, most sensors or input devices (like switches, temperature sensors, or pressure sensors) do not work on just 5V DC.
That’s why we need the Input Module. Its main jobs are:
To adjust the signals from sensors so that the CPU always receives a safe 5V DC signal.
To convert analog signals into digital signals, because the CPU can only understand digital (ON/OFF) signals, while many sensors produce analog signals.
On the other side, the CPU output is also very weak. It can only supply a tiny current at 5V DC, which is not enough to run real devices like motors, lamps, relays, or actuators.
This problem is solved by the Output Module, which takes the small signal from the CPU and then provides the proper voltage and current needed to run the output devices safely.
Power Supply
The power supply unit of a PLC provides the required power to all its parts, including the CPU, memory, input module, and output module.
PLC systems usually work with standard voltage levels such as 24V DC, 120V AC, or 240V AC, depending on their design and use.
For example, if the PLC is designed to run on 24V DC, then you must use a 24V DC power converter to make sure the PLC operates properly.
What we learn today?
From the above block diagram, you can now easily understand the working principle of a PLC system. One of the main reasons PLCs are so popular in industries is because of their many advantages.
The key advantages of using a PLC are:
High efficiency – PLCs make industrial automation more reliable and effective.
Fast operation – They can process signals and respond very quickly.
Advanced control – PLCs can handle not only basic tasks but also complex operations.
Easy to use – They are user-friendly, and once you learn the basics, working with PLCs is simple.
Automatic control – The ability to fully automate machines and processes is one of the biggest benefits.

