Table of Contents
TogglePiezoresistive vs Piezoelectric Pressure Sensors: Introduction
When selecting a pressure sensor, engineers often face one common question:
Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric — which technology should I choose?
At first glance, both sensors look similar. Both measure pressure. Both are used in industrial and research applications. But in reality, the difference between Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric technology is significant especially when it comes to static pressure, dynamic pressure, accuracy, and response time.
Choosing the wrong sensor can lead to unstable readings, signal drift, or even complete measurement failure.
In this article, we will clearly understand the difference between Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric pressure sensors so students, technicians and engineers can confidently select the right technology.
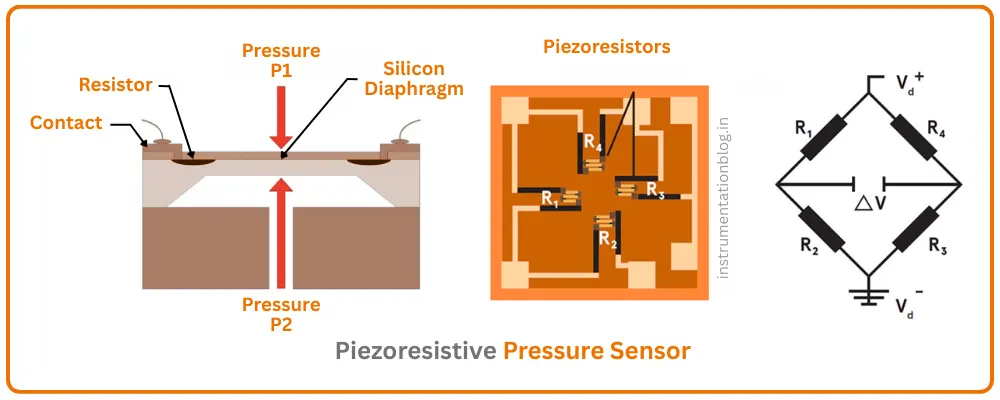
What Is a Piezoresistive Pressure Sensor?
A piezoresistive pressure sensor works on a simple principle:
When pressure is applied to a diaphragm, the diaphragm bends slightly. This bending changes the electrical resistance of silicon strain gauges mounted on it.
This resistance change is measured using a Wheatstone bridge circuit, which converts the tiny resistance variation into a measurable voltage signal.
Key Characteristics
Measures static and dynamic pressure
It can measure steady pressure like water in a pipeline.Requires external power supply
The bridge circuit needs excitation voltage.Very small sensor size
MEMS technology allows extremely compact designs.High accuracy
Typical accuracy ranges from 0.1% to 1.0% of full scale.
Common Applications
Process pressure transmitters
Hydraulic systems
Oil & gas pipelines
Water treatment plants
HVAC systems
When comparing Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric, the piezoresistive sensor is the dominant choice in industrial process measurement.
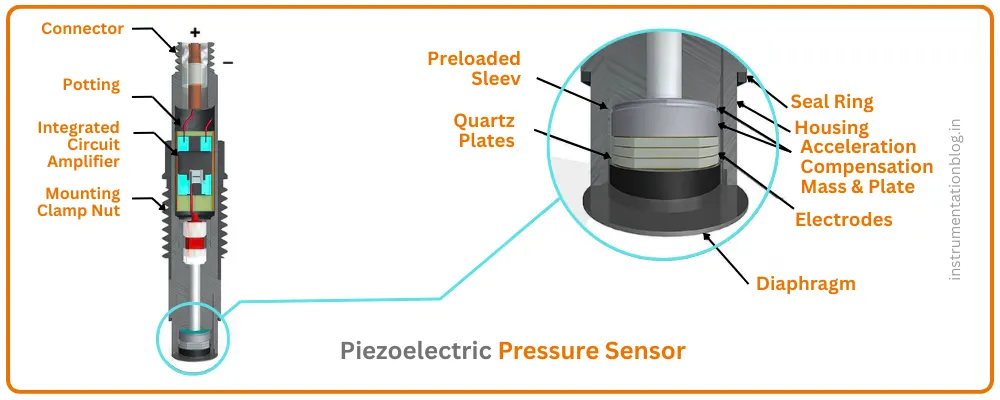
What Is a Piezoelectric Pressure Sensor?
A piezoelectric pressure sensor works differently.
It uses a special crystal material (like quartz). When pressure is applied, the crystal generates an electrical charge. This effect is called the piezoelectric effect.
Unlike piezoresistive sensors, piezoelectric sensors generate their own signal when stressed.
Key Characteristics
Best for dynamic pressure
Ideal for rapidly changing pressure.Cannot measure true static pressure
The generated charge leaks over time.Extremely fast response
Excellent high-frequency performance.Moderate accuracy
Typically 1% to 3% of full scale.
In the discussion of Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric, piezoelectric sensors are the preferred solution for fast, high-speed events.
Static Pressure Capability – The Biggest Difference
The most important difference in Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric comparison is static pressure measurement.
1 Piezoresistive Sensors and Static Pressure
Because the measurement is based on resistance change, the signal remains stable as long as pressure is applied.
This makes piezoresistive sensors ideal for:
Tank level pressure
Boiler pressure
Compressed air systems
Pipeline pressure
2 Piezoelectric Sensors and Static Pressure
Piezoelectric sensors generate electrical charge when pressure changes. But if pressure remains constant, the charge slowly dissipates.
This means:
They cannot accurately measure steady pressure.
They are unsuitable for process industry applications.
In any Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric selection for static applications, piezoresistive wins clearly.
Dynamic Pressure Measurement
Now let’s reverse the situation.
When pressure changes extremely fast, such as explosions or combustion the comparison of Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric shifts.
1 Piezoresistive Sensors
Good for low-frequency changes
Limited high-frequency response
Suitable for slow or moderate pressure variation
2 Piezoelectric Sensors
Excellent high-frequency response
Can measure rapid pressure spikes
Ideal for engine combustion testing
Used in shock wave measurement
For high-speed applications, the answer to Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric is almost always piezoelectric.
Accuracy Comparison
Accuracy plays a major role in the Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric decision.
Piezoresistive Accuracy
Typically 0.1% to 1.0% FS
Very stable for steady-state measurement.Piezoelectric Accuracy
Typically 1.0% to 3.0% FS
Designed more for waveform capture than absolute accuracy.
If your process requires precise control, the Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric comparison favors piezoresistive sensors.
Overpressure Capability
Both technologies can handle high overpressure sometimes 2X to 50X of rated pressure.
However:
Mechanical design matters more than sensing principle.
Protection design determines survivability.
In most practical cases, Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric overpressure capability depends on manufacturer design.
Size and Construction
Modern MEMS fabrication allows piezoresistive sensors to be extremely compact as small as 0.055 inches.
Piezoelectric sensors are typically larger (around 0.19 inches or more) due to crystal and housing structure.
In portable or space-limited designs, the Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric comparison favors piezoresistive technology.
Power Requirement
Piezoresistive
Requires excitation voltage.Piezoelectric
Self-generating signal (but requires signal conditioning amplifier).
This is another important factor in Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric evaluation.
Application Selection Guide
To simplify the Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric decision:
Need steady pressure measurement?
Choose Piezoresistive.Need explosion or combustion measurement?
Choose Piezoelectric.Need high accuracy process control?
Choose Piezoresistive.Need very fast pressure spike measurement?
Choose Piezoelectric.Industrial transmitter application?
Piezoresistive dominates.
Comparison Table: Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric Sensors
| Parameter | Piezoresistive Sensors | Piezoelectric Sensors |
|---|---|---|
| How They Work | Measure resistance changes in silicon under stress. | Generate electric charge when crystals are squeezed. |
| Static Pressure | Can measure steady pressure (e.g., tire pressure). | Only measures changing pressure (e.g., engine combustion). |
| Accuracy | 0.1%-0.5%-1.0%/FS | 1.0%-2.0%-3.0%/F |
| Overpressure | 2X to 50X | 2X to 50X |
| Size | Tiny (as small as 0.055″ diameter). | Bulky (smallest is ~0.19″ diameter). |
| Temperature Range | -320°F to 1000°F (unamplified). | -320°F to 1040°F (limited by crystal type). |
| Vibration Sensitivity | Low (0.00015 PSI/g). | High (0.002 PSI/g). |
| Cost (Sensor) | Low-Medium XX | Medium-High XXX |
| Cables | Standard shielded wires (cheap). | Special low-noise cables (expensive). |
| Durability | Rugged, ideal for harsh environments. | Sensitive to installation errors and shock. |
| Power Needs | Requires external power (5–15V) | Self-powered (no external juice needed) |
| Signal Output | Voltage (0–10V) or current (4–20mA). | Charge or voltage (needs amplifiers). |
| Industry Applications |
|
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the main difference between Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric pressure sensors?
The main difference in Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric sensors lies in how they generate signals. Piezoresistive sensors measure pressure by detecting resistance changes in silicon strain gauges, making them suitable for static and steady pressure. Piezoelectric sensors generate electrical charge when pressure changes, making them ideal for dynamic or rapidly changing pressure measurements.
2. Can piezoelectric sensors measure static pressure?
No. In the Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric comparison, piezoelectric sensors cannot accurately measure static pressure because the electrical charge they generate leaks over time. They are best suited for dynamic pressure such as vibration, combustion, or shock waves.
3. Which sensor is more accurate: Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric?
When comparing Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric, piezoresistive sensors are generally more accurate for steady-state industrial applications, with accuracy typically between 0.1% and 1.0% of full scale. Piezoelectric sensors usually have 1% to 3% accuracy and are optimized for capturing rapid pressure changes rather than precise static readings.
4. Where are piezoresistive pressure sensors commonly used?
In the Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric discussion, piezoresistive sensors are widely used in process industries such as oil & gas, water treatment, HVAC, hydraulics, and industrial automation. They are ideal for continuous pressure monitoring and control systems.
5. When should I choose a piezoelectric pressure sensor?
In the Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric selection process, you should choose a piezoelectric sensor when measuring high-speed dynamic pressure events such as engine combustion, explosion testing, ballistic pressure measurement, or shock wave detection.
6. Do piezoresistive and piezoelectric sensors require external power?
In the Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric comparison, piezoresistive sensors require an external excitation voltage because they operate using a Wheatstone bridge circuit. Piezoelectric sensors generate their own electrical charge, but they still require signal conditioning electronics or amplifiers for proper output measurement.
What we learn today?
The debate of Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric is not about which technology is better.
It is about application suitability.
For industrial static pressure → Piezoresistive
For dynamic high-speed pressure → Piezoelectric
Understanding the difference between Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric ensures accurate measurement, system stability, and reliable process control.
Selecting the correct technology is not optional it is critical for engineering success.
I hope you like above blog. There is no cost associated in sharing the article in your social media. Thanks for Reading !! Happy Learning