Table of Contents
ToggleMetal Tube Rotameter –Introduction
Flow measurement in industrial plants is not always simple. In many applications, the fluid is hot, under high pressure, corrosive, or opaque. In such cases, a normal glass rotameter may not survive.
This is where a metal tube rotameter becomes the preferred solution.
In this article, let us understand its working principle, formula, construction, benefits, and real industrial applications.
What is a Metal Tube Rotameter?
A metal tube rotameter is a type of variable area flow meter used to measure the flow rate of liquids and gases in industrial processes.
Unlike glass rotameters, which are suitable for low pressure and visible fluids, metal tube rotameters are specially designed for:
High-pressure applications
High-temperature services
Turbid or opaque fluids
Chemically aggressive environments
Hazardous or explosion-prone areas
Because the measuring tube is made of metal, it provides superior mechanical strength and process safety. These instruments are widely used in oil & gas, chemical plants, power plants, and heavy industries.
In simple words, when the process becomes rugged, the metal tube rotameter becomes the right choice.
Working Principle of Metal Tube Rotameter
The metal tube rotameter works on the variable area principle.
At the heart of the instrument, there are two main parts:
A vertically mounted tapered metal tube
A freely moving float inside the tube
Let us understand step by step how it works.
The process fluid enters the rotameter from the bottom and flows upward through the tapered tube.
Initially, the float rests at the bottom due to gravity.
As the fluid flows upward, it exerts an upward force on the float.
The float rises until the upward force caused by flow equals the downward gravitational force of the float.
At this equilibrium position, the float stabilizes. The height of the float corresponds directly to the flow rate.
As the tube is tapered, the area between the float and tube wall increases as the float rises. Higher flow means higher float position.
This balance condition defines the flow measurement.
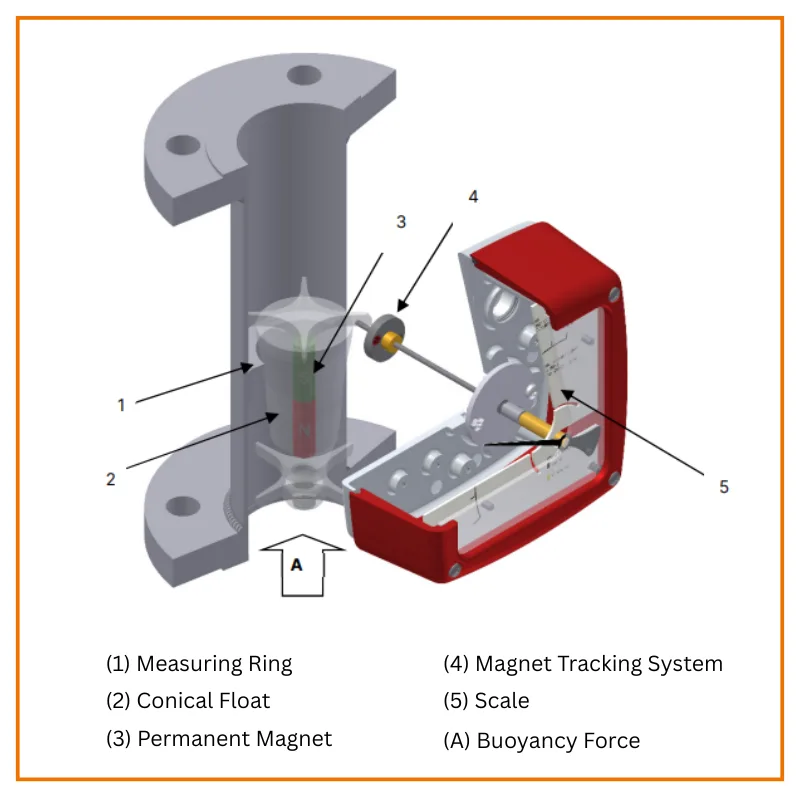
Please see below figure showing different parts of metal tube rotameter.
The measuring element consists of a sharp-edged measuring ring (1) and a conical float (2). A medium flows from the bottom to the top through the measuring ring, lifting the float until the buoyancy force (A) and the weight of the float establish equilibrium.
As the height of the float varies, an annular clearance proportional to the flow appears between the float and the measuring ring. The height of the float in the measuring ring is a measure of the flow. The permanent magnet (3) embedded in the float then transmits this measure to the scale (5) and by means of a magnet tracking system (4) to the optional electronic evaluation devices.
Basic Rotameter Formula
One simplified formula used in rotameters is:
Q = kA√(gH)
Where:
Q = volumetric flow rate
k = constant
A = annular area between float and tube
g = acceleration due to gravity
H = pressure drop across the float
This equation shows that flow rate depends on the annular area and pressure drop around the float.
How Flow is Indicated in Metal Tube Rotameter
In a glass rotameter, the float position is visible directly.
But in a metal tube rotameter, the tube is not transparent. So how do we read the flow?
There are two common methods.
Magnetic Coupling System
The float inside the tube contains a magnet. Outside the tube, a follower magnet tracks the float position. This movement is mechanically linked to a pointer and scale.
As the float moves up or down, the external indicator shows the flow rate.
Electronic Display System
Modern metal tube rotameters use magnetic sensors and chip technology.
These advanced models can provide:
Instantaneous flow
Totalized (accumulated) flow
Percentage flow
LCD display
4–20 mA output
HART communication
Because the magnetic coupling has no direct mechanical penetration through the tube, leakage risk is eliminated and signal transmission remains stable.

Main Elements of a Metal Tube Rotameter
Let us understand its construction clearly.
1. Tapered Tube
The tube is metallic and gradually widens from bottom to top.
This taper ensures that different flow rates correspond to different float positions.
The tube material is usually stainless steel or special alloys for corrosive services.
2. Float
The float is precisely designed and often made of stainless steel or corrosion-resistant material.
Its weight and shape are carefully engineered to maintain stable equilibrium during operation.
3. Magnetic Coupling
The magnetic system transfers float position to the external indicator.
It ensures:
Leak-proof design
High reliability
Safe operation in hazardous areas
4. Indicator Mechanism
The indicator may be:
Analog pointer scale
LCD digital display
Remote transmitter with alarm settings
Advanced versions allow setting upper and lower alarm limits easily.
Benefits of Using Metal Tube Rotameter
Now let us see why industries prefer metal tube rotameters.
-
High Durability
The metallic body withstands mechanical stress and vibration.
-
High Pressure and Temperature Resistance
Suitable for steam, hydrocarbons, and hot process fluids.
-
Chemical Resistance
Works well with aggressive chemicals when proper materials are selected.
-
Suitable for Opaque Fluids
Even if the fluid is dark or dirty, measurement remains accurate.
-
Explosion-Proof Design
Many models are certified for hazardous areas.
-
Multiple Output Options
Supports 4–20 mA, pulse output, and HART protocol.
-
Alarm Functionality
Upper and lower alarm limits can be configured.
-
High Accuracy and Repeatability
One-time roll forming sensors provide stable and repeatable measurement.
Industrial Applications of Metal Tube Rotameter
Metal tube rotameters are widely used across industries.
1. Oil and Gas Industry
Used to measure crude oil, natural gas, condensate, and other hydrocarbons.
Because of their ability to handle high pressure, they are suitable for pipelines and wellhead services.
2. Chemical Industry
Used for corrosive chemicals, acids, and solvents.
Material selection plays a crucial role here.
3. Wastewater Treatment
Measures water flow and chemical dosing for pH control and disinfection.
4. Pharmaceutical Industry
Used in controlled processes for solvents and purified water systems.
5. Food and Beverage Industry
Sanitary versions are used to measure additives and ingredients in processing lines.
Installation Guidelines
Proper installation is critical for accuracy.
The metal tube rotameter must be installed vertically.
Flow direction should always be from bottom to top.
Horizontal installation is possible only in special designs and must be specified during ordering.
The instrument should be rigidly mounted to avoid vibration.
Isolation valves should be provided to protect the meter from sudden pressure surges.
Calibration Considerations
Calibration ensures measurement reliability.
Calibration should be done using a fluid with similar density and viscosity as the process fluid.
Many manufacturers provide factory calibration certificates.
Field calibration can be done using certified flow standards.
In magnetic systems, alignment between float magnet and external magnet must be correct. Misalignment leads to inaccurate readings.
What we learn today?
A metal tube rotameter is one of the most reliable and rugged flow meters available for industrial applications.
When you need:
Strength
High pressure resistance
High temperature tolerance
Chemical compatibility
Explosion-proof safety
This flow meter becomes a strong candidate.
In simple words, if a glass rotameter cannot survive in your process, a metal tube rotameter probably can.
Choosing the correct material, proper installation, and suitable calibration will ensure long-term stable and accurate performance.
And as always in instrumentation, the right selection depends on understanding the process conditions clearly before finalizing the instrument.
I hope you like above blog. There is no cost associated in sharing the article in your social media. Thanks for Reading !! Happy Learning