Table of Contents
ToggleNitrogen Purging: Introduction
In many industrial processes, controlling oxygen and moisture is not optional but it is critical.
Even small amounts of air or water vapor inside a system can lead to corrosion, oxidation, product degradation, fire risk, or poor process quality.
This is where nitrogen purging is used.
Nitrogen purging is widely used across industries such as oil & gas, chemicals, power plants, electronics, food processing, pharmaceuticals and metal fabrication.
Its main purpose is simple: replace air with an inert, dry, non-reactive gas => nitrogen (N₂).
1. What Is Nitrogen Purging?
Nitrogen purging is a process in which nitrogen gas is introduced into a system to displace unwanted gases, mainly oxygen, moisture, and contaminants.
Instead of leaving air inside vessels, pipelines, tanks, or equipment, nitrogen is used to create a controlled inert atmosphere.
This is important because:
Oxygen supports oxidation and combustion
Moisture causes corrosion, rust, and microbial growth
Air contains contaminants that can damage sensitive processes
Nitrogen is ideal because it is:
Chemically inert
Dry
Non-flammable
Readily available
Cost-effective for industrial use

2. Why Nitrogen Is Used for Purging
Nitrogen makes up about 78% of atmospheric air, but when supplied industrially, it is clean, dry, and controlled.
The main objectives of nitrogen purging include:
Inerting
Nitrogen does not react with most substances. Replacing air with nitrogen removes oxygen and reduces the risk of fire, explosion, or unwanted chemical reactions.Oxygen Removal
Many materials degrade quickly in the presence of oxygen. Nitrogen purging protects products, equipment, and pipelines by keeping oxygen levels low.Moisture Control
Nitrogen is extremely dry. Purging helps remove water vapor, preventing corrosion, condensation, mold growth, and freeze damage.Contaminant Removal
Dust, vapors, fumes, and residual gases are flushed out, creating a clean internal environment.
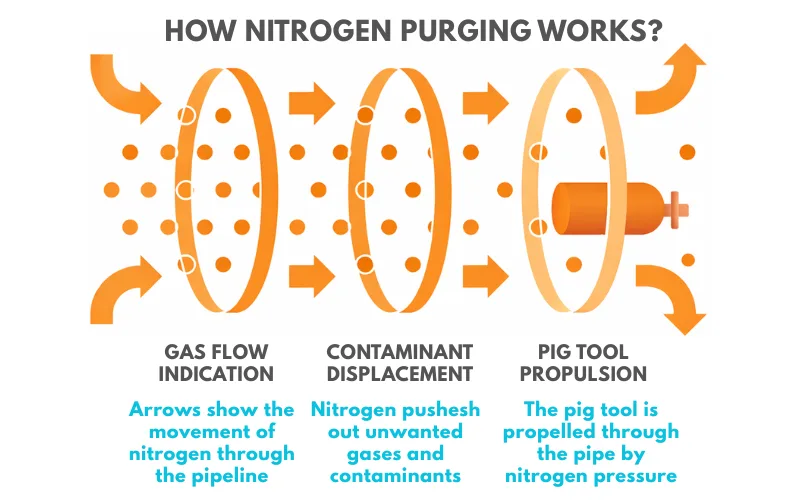
3. How Nitrogen Purging Works (Basic Principle)
Nitrogen purging works by replacing oxygen and other hazardous gases with inert nitrogen. As nitrogen enters the system, it forces the existing gases out, creating a safe and non-reactive environment.
The working principle of nitrogen purging is straightforward.
Nitrogen gas is introduced into the system through an inlet
The nitrogen pushes out existing air or process gases
Displaced gases exit through a vent or outlet
Over time, oxygen concentration drops to a safe or required level
Depending on the method used, nitrogen may:
Completely displace air
Dilute air gradually
Pressurize and vent repeatedly
The final result is a nitrogen-rich, low-oxygen environment.
Nitrogen is commonly used for oxygen displacement because it is inert, easy to source, and does not react with process materials or equipment.
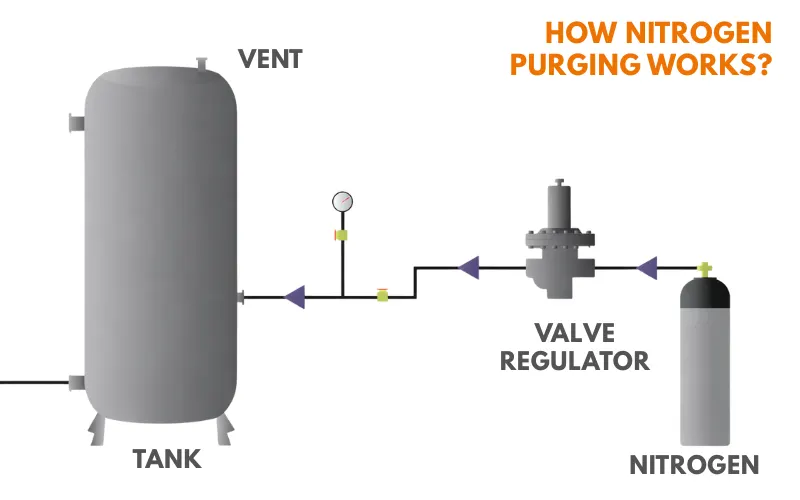
4. How Nitrogen Purging Differs from Other Purging Methods
Not all purging methods are the same. Each has advantages and limitations.
Steam Purging
Steam is effective for cleaning but introduces moisture. It is unsuitable for moisture-sensitive systems and often requires drying afterward.Vacuum Purging
Vacuum systems remove gases by suction. While effective, they require expensive equipment and may not work well for large volumes.Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) Purging
CO₂ displaces oxygen but can be corrosive and may introduce moisture. It is less inert than nitrogen in many applications.
Nitrogen remains the preferred choice because it is dry, inert, safe, and process-friendly.
5. Why Nitrogen Purging Is Necessary in Industry
Nitrogen purging is not just a best practice—it is often a safety and quality requirement.
Without purging:
Oxygen causes oxidation and corrosion
Moisture leads to rust and microbial growth
Flammable environments become dangerous
Product quality degrades
Equipment life is reduced
Nitrogen purging ensures:
Process stability
Extended equipment life
Improved product consistency
Safer working conditions
6. Common Industrial Applications of Nitrogen Purging
Nitrogen purging is used across many industries, including:
Oil & Gas
Used for pipeline commissioning, tank blanketing, and explosion prevention.Chemical & Petrochemical Plants
Removes oxygen to prevent unwanted reactions and degradation.Power & Electrical Systems
Protects transformers and switchgear from moisture and oxidation.Food & Beverage Industry
Used in modified atmosphere packaging to extend shelf life.Breweries
Purges oxygen from tanks and headspaces to preserve flavor.Electronics Manufacturing
Prevents oxidation during soldering and semiconductor processes.Metal Fabrication & Welding
Improves weld quality by eliminating oxygen contamination.
7. Four Types of Nitrogen Purging Systems
Different systems require different purging techniques.
7.1 Displacement Purging
Nitrogen directly pushes air out of the system.
Best for pipelines and simple vessels.
7.2 Dilution Purging
Nitrogen mixes with existing gases and gradually reduces oxygen concentration.
Suitable for complex equipment like reactors and columns.
7.3 Pressure Liquid Transfer
Nitrogen pressurizes a vessel to move liquids without pumps.
Reduces oxidation during transfer.
7.4 Pressure-Hold Vacuum Method
Repeated pressurization and venting cycles reduce oxygen levels.
Used when only one vent point is available.
8. Factors That Affect Nitrogen Purging Efficiency
Several parameters influence how effective purging will be:
Pressure & Flow Rate
Too low leads to incomplete purging; too high creates turbulence.Inlet and Outlet Positioning
Incorrect placement causes trapped air pockets.System Geometry
Dead legs and complex piping require special attention.Temperature
Cold conditions may affect nitrogen behavior and density.Nitrogen Purity
Higher purity ensures better oxygen displacement.
9. Nitrogen Purging in Pipelines
Pipeline purging is essential during:
New pipeline commissioning
Maintenance shutdowns
Product changeovers
Nitrogen removes:
Oxygen
Moisture
Dust and debris
This prevents corrosion, flow issues, and safety hazards before the pipeline is put into service.
10. Safety Considerations During Nitrogen Purging
Nitrogen is safe but oxygen-deficient environments are not.
Key safety measures include:
Proper personnel training
Use of oxygen monitors
Clear ventilation paths
Emergency shutdown procedures
Mandatory PPE
Strict work permits and supervision
Nitrogen purging should always be treated as a controlled operation, not a routine task.
What we learn today?
Nitrogen purging is one of the most reliable and widely used techniques for controlling oxygen, moisture, and contamination in industrial systems.
Whether it is a pipeline, vessel, transformer, or packaging line, nitrogen purging ensures:
Safety
Product integrity
Process efficiency
Equipment protection
When designed and executed correctly, nitrogen purging becomes a silent guardian of industrial reliability.
I hope you like above blog. There is no cost associated in sharing the article in your social media. Thanks for Reading !! Happy Learning



