In industries like oil & gas, chemicals, water treatment & power plants, measuring the level of liquids in tanks and vessels is extremely important. The instruments used for this purpose are called level gauges.
Level gauges tell us how much liquid is inside a container, and help operators decide when to fill, empty, or monitor a tank for safety. Choosing the correct type of level gauge depends on the liquid, the operating conditions, and the safety needs.
Here, we will go through the main types of level gauges and also share useful tips and tricks to understand when and how to use them effectively.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Sight Glass Level Gauge
This is the simplest level gauge. It uses a transparent glass tube connected to the tank so that the liquid inside rises to the same height in the tube.
Tips & Tricks:
- Always install a protective guard around the glass tube to prevent accidental breakage.
- For hot fluids, use heat-resistant glass to avoid cracking.
- Clean the glass regularly so the level is clearly visible.
- Ideal for small tanks like water or storage drums where safety risks are low.
2. Reflex Level Gauge
A reflex gauge has special prism glass that makes the liquid look dark and the vapor look bright. This contrast helps in easy reading.
Tips & Tricks:
- Reflex gauges are a great choice for boilers. They provide a clear level reading even when pressure and temperature are high.
- Avoid using reflex gauges with colored liquids because the dark/bright contrast effect won’t work.
- If visibility is poor, install side lighting to make the level more visible.
- Good option when you want low maintenance and high durability.
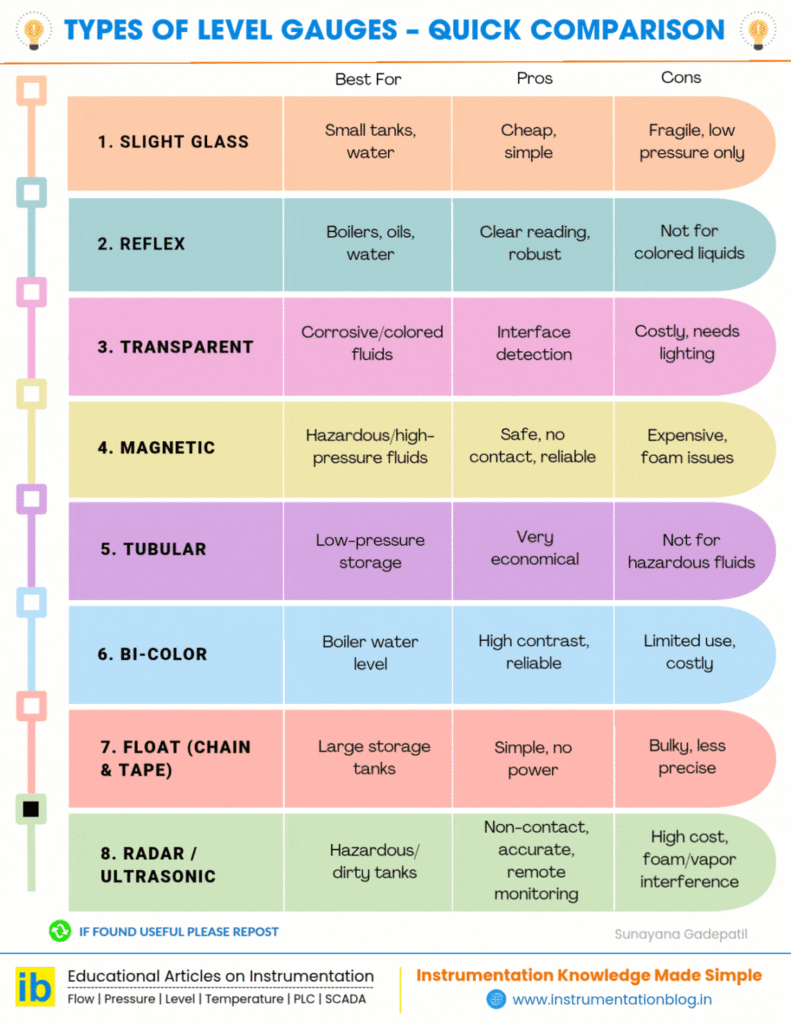
3. Transparent Level Gauge
This gauge has two glass plates so you can see the liquid directly between them.
Tips & Tricks:
- Best for colored or corrosive fluids because you see the actual color of the liquid.
- Works well when you need to monitor the interface between two liquids (e.g., oil and water).
- To improve visibility, place the gauge in a well-lit area or use a backlight.
- Always use protective shields when dealing with aggressive chemicals.
4. Magnetic Level Gauge
In this type, a float with a magnet moves with the liquid. Outside the tank, magnetic flaps or an indicator follow the float to show the level.
Tips & Tricks:
- Use magnetic gauges when handling hazardous, toxic, or high-pressure fluids. The indicator is outside, so it is very safe.
- Great for remote sites since they need very little maintenance.
- To avoid false readings, keep them away from external strong magnets.
- If you deal with foamy liquids, add still pipes inside the tank to ensure stable float movement.
5. Tubular Level Gauge
This is similar to a sight glass but longer and usually used for larger tanks.
Tips & Tricks:
- Best suited for low-pressure storage tanks.
- Use valves at top and bottom so the gauge can be isolated for cleaning without draining the tank.
- Apply anti-corrosion coating to the metal fittings if the liquid is slightly aggressive.
- Regularly check the sealing gaskets to prevent leaks.
6. Bi-Color Level Gauge
This gauge uses two colors (red and green lights) to clearly show water and steam levels in boilers.
Tips & Tricks:
- Very useful in power plants where boiler safety is critical.
- Always check the illumination system (LED or lamp) to ensure proper visibility.
- For best results, install in pairs with a reflex gauge for backup reading.
- Train operators to read bi-color gauges correctly since colors may look different in bright sunlight.
7. Float (Chain & Tape) Level Gauge
Here, a float rests on the liquid, and its movement is transferred via chain and pulley to an external scale.
Tips & Tricks:
- Perfect for large storage tanks like fuel, water reservoirs, or oil tanks.
- Always ensure the pulley system is well lubricated to prevent wear and tear.
- Install a dust cover on the tape and pulley to avoid dirt buildup.
- Remember: This is a mechanical system, so it needs regular inspection.
8. Radar and Ultrasonic Level Gauges
These are electronic gauges that use radar or ultrasonic waves to measure liquid levels without touching the liquid.
Tips & Tricks:
- Ideal for hazardous, corrosive, or dirty liquids since there is no direct contact.
- If there’s foam on the liquid, use guided wave radar instead of free-space radar for better accuracy.
- Always ensure the antenna or sensor is clean to prevent signal blockage.
- If you need remote monitoring, these gauges can be connected to digital control systems like SCADA.
Master Tips for Choosing the Right Level Gauge
- Know Your Liquid – Is it clear, colored, corrosive, foamy, or hazardous? This decides which gauge works best.
- Consider Pressure & Temperature – Reflex and bi-color are excellent for boilers; tubular and sight glass are better for low-pressure tanks.
- Think About Safety – For toxic or explosive fluids, magnetic and radar gauges are safest.
- Check Maintenance Needs – Mechanical gauges need cleaning and inspection, while electronic ones need power supply and calibration.
- Budget Wisely – Simple gauges like sight glass are low-cost, but modern radar gauges, while expensive, provide high safety and accuracy.
What we learn today?
Level gauges are simple yet powerful tools that keep industries running safely and efficiently. From the basic sight glass to the advanced radar system, each type has its place.
By using the tips and tricks shared here, technicians and engineers can:
- Select the right gauge for the right job.
- Maintain gauges properly for longer life.
- Improve safety and efficiency in their plants.
Remember:
- Use sight glass or tubular for simple applications.
- Choose reflex or transparent for boilers or colored fluids.
- Go with magnetic for hazardous liquids.
- Pick radar/ultrasonic when you need accuracy, safety, and remote monitoring.
With the right knowledge, selecting and maintaining a level gauge becomes easy, safe, and efficient.
I hope you like above blog. There is no cost associated in sharing the article in your social media. Thanks for reading!! Happy Learning!!



